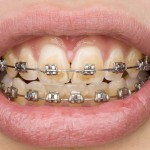
51 studies were included in this Cochrane review of chlorhexidine mouthwash as an adjunct to mechanical oral hygiene measures. The review provides high quality evidence for a large reduction in the build-up of plaque at 4 to 6 weeks or 6 months. There is also high quality evidence of a moderate reduction in gingivitis in patients with mild gingivitis which may not be clinically important.
[read the full story...]