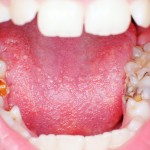
Early childhood caries (ECC) is a common oral health problem, particularly in disadvantaged and developing populations. Its causes are multifaceted, including feeding practices like breastfeeding. The link between breastfeeding and ECC is unclear. Key findings No significant association was found between breastfeeding and the development of early childhood caries (ECC). Nighttime breastfeeding was associated with an [read the full story…]