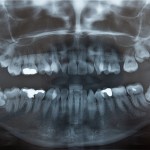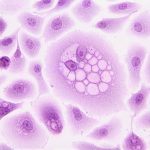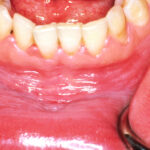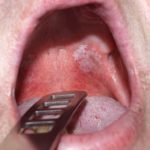
Antiresorptive drugs, used to treat osteoporosis and metastatic bone disease, can complicate dental implant procedures by increasing the risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). This systematic review investigates how these drugs affect the success and complications associated with osseointegrated dental implants. Key findings Antiresorptive drugs significantly increase the risk of (MRONJ), accounting for [read the full story…]