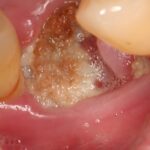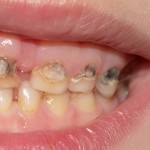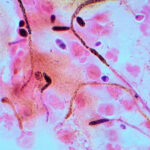
This review comparing the efficacy and safety of topical antifungal drugs for oral candidiasis in children and adults included 11 RCTs 9 of which concerned adults and 2 children. The findings support the use of fluconazole and amphotericin B for adults.
[read the full story...]