
In their debut blog, Grace Williamson and Daniel Leightley review a US study on chronic pain, cannabis legalisation, and cannabis use disorder in US veterans.
[read the full story...]
In their debut blog, Grace Williamson and Daniel Leightley review a US study on chronic pain, cannabis legalisation, and cannabis use disorder in US veterans.
[read the full story...]
This review comparing the effectiveness of articaine and lidocaine for lower third molar surgery included 14 RCTs. The findings suggest that articaine is superior to lidocaine for use in lower third molar however the available are small so additional larger high quality studies would be helpful to strengthen the evidence.
[read the full story...]
Ed Palmer considers new research on the genetic risk for Tourette Syndrome and it’s relationship to other mental and physical health conditions.
[read the full story...]
This review to evaluate the effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on burning pain, quality of life, and negative emotions in patients with burning mouth syndrome included 14 RCTs only two of which were at low risk of bias.While the findinds suggest that LLLT has a positive effect the quality of evidence means the findings should be interpreted cautiously.
[read the full story...]
This review comparing patient-related outcomes of intraoral scanning and conventional impression methods included 13 studies. Nine of the included studies were RCTs and all were considered to be at unclear risk of bias. The findings indicated a patient preference for digital scanning over conventional impression techniques.
[read the full story...]
This review of the effects of photobiomodulation (PBM) on pain, oedema, and trismus after extraction of impacted mandibular third molars included 33 RCTs. However 30 of the included studies were considered to be at high risk of bias, and while the results suggested small benefits for PBM in relation to reduction of pain and swelling these were not considered to be clinically important.
[read the full story...]
This review of the efficacy of chewing gum in reducing pain intensity in patients undergoing fixed orthodontic treatment included 16 RCTs. The findings suggest , chewing gum was significantly more effective than both pharmacologic agents and placebo in reducing orthodontic pain 24 hours. However the evidence is of very low certainty.
[read the full story...]
This review and network meta-analysis (NMA) of pharmacological treatments for the management of pain subsequent to simple and surgical tooth extraction included 85 RCTs. There was moderate- and high-certainty evidence that for surgical dental extractions that ibuprofen 200 to 400 mg plus acetaminophen 500 to 1,000 mg was the most effective for pain relief.
[read the full story...]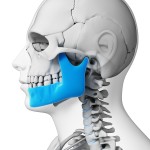
This review of temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis versus conservative management for painful temporomandibular disorders (TMD) includes 7 RCTs. The findings suggest improvements in both pain and maximum mouth opening with arthrocentesis but these may not be clinically important.
[read the full story...]
This review assessing the effect of disocclusion guidance on occlusal splints for sleep bruxism (SB) and temporomandibular disorders (TMD) included 15 studies. The included studies provided very low certainty evidence for most of the evaluated outcomes.
[read the full story...]