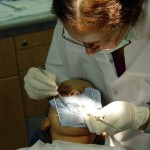
This review of the effects and adverse reactions between articaine and lidocaine in paediatric dental procedures included 8 RCTS. Three of the included studies were at high risk of bias 2 at low risk and 3 at unclear risk. The findings suggested no difference in adverse effects between the two anaesthetics with the certainty of evidence being assessed as moderate.
[read the full story...]