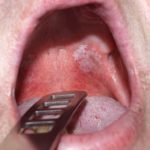
Oral leukoplakia is one of a number of oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMD) with a 2018 review (Dental Elf – 8th Aug 201) estimating a prevalence of 4.11% (95%CI; 1.98 to 6.97%). A number of studies and reviews have reported on the malignant transformation rate in oral leukoplakia most recently in 2021 (Dental Elf – 25th Jun 2021).
The aim of this review was to assess the rate of malignant transformation (MT) of oral leukoplakia (OL) and to study potential risk factors for the MT of OL into oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods
With a protocol registered on the PROSPERO searches were conducted in the PubMed/Medline ScienceDirect, Web of Science, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Science and Technology Journal Database (CQVIP), Wanfang Data, and the Chinese Science Citation Databases from January 2000 to March 202. Chinese and English language, cohort studies, large case series, clinical trials and experimental studies and case reports or case series of OL with available histopathological reports by biopsy at initial diagnosis were considered. Two reviewers independently selected studies, extracted data and assessed study quality using a modified version of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) tool. Estimates of MT rate and odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals were calculated and a random effects meta-analyses conducted.
Results
- 26 studies reporting on 6486 cases of OL were included.
- 5 studies were considered to be at moderate risk of bias and 21 at low risk.
- OSCC developed in 392 out of the 6486 cases.
- Meta-analyses (26 studies) found an overall malignant transformation rate = 7.2% (95%CI; 5.40 to 9.10%).
- Odds ratios for MT for dysplasia type, clinical subtype and clinical site are shown in the table below.
| No. of studies | Odds ratio for malignant transformation (95%CI) | |
| Mild dysplasia | 10 | 1.87 (0.73 to 4.76) |
| Moderate dysplasia | 10 | 2.93 (1.62 to 7.35) |
| Severe dysplasia | 10 | 7.13 (1.81 to 5.45) |
| Non-homogenous leukoplakia | 6 | 4.93 (1.71 to 14.28) |
| Palate | 10 | 2.10 (0.73 to 6.07) |
| Buccal | 10 | 2.19 (0.95 to 5.05) |
| Tongue | 10 | 6.38 (3.24 to 12.56) |
| Lip | 4 | 4.26 (0.96 to 18.83) |
| Floor of mouth | 6 | 3.75 (1.32 to 10.67) |
| Multifocal | 2 | 8.58 (1.39 to 5.77) |
- 12 studies reported on smoking status and 8 on alcohol consumption but no statistically significant differences were seen.
- Only 1 study reported on betel nut chewing.
Conclusions
The authors concluded: –
… the pooled proportion of the MT of OL was 7.20%. Higher grades of dysplasia, the nonhomogeneous type, the location of the lesions (tongue and multifocal), and female sex had significant effects on the MT of OL. Considering the limitations of this study, prospective studies on a larger scale are required to validate our results, with unified clinicopathological diagnostic criteria, standardized risk factor recording/ assessment methods, and long-term follow-up guidelines.
Comments
A protocol was registered for this review and a good range of databases searched. Inclusions were restricted to Chinese and English language papers so it is possible that some relevant papers may have been excluded. One of aims of this review was to update and earlier review by Warnakulasuriya and Ariyawardana which we have looked at previously (Dental Elf – 24th Jul 2015) along with an update published in 2021 by Aguirre-Urizar et al (Dental Elf – 25th Jun 2021). The 2021 review included 24 studies (16,604 patients) and this new review included 26 (6,486 patients) with only 5 studies common to both reviews. The pooled MT rate of OL in the Aguirre-Urizar et al review was 9.8% (95%CI; 7.9 to 11.7%) compared with 7.2% (95%CI; 5.40 to 9.10%)in this review. Issues related to the diagnostic criteria for oral leukoplakia, sample sizes and follow-up time all contribute to heterogeneity in the available studies and the bulk of the included studies are also retrospective in nature. As noted by the authors larger scale prospective studies using common diagnostic criteria, assessment criteria and long-term follow-up would be needed to improve the available evidence.
Links
Primary Paper
Guan JY, Luo YH, Lin YY, Wu ZY, Ye JY, Xie SM, Li J. Malignant transformation rate of oral leukoplakia in the past 20 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2023 May 24. doi: 10.1111/jop.13440. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37224426.
Other references
Dental Elf – 8th Aug 2018
Dental Elf – 25th Jun 2021
Dental Elf – 24th Jul 2015
Oral leukoplakia: malignant transformation rate highly variable
Picture credits
By Klaus D. Peter, Gummersbach, Germany – Own work, CC BY 3.0 de,
