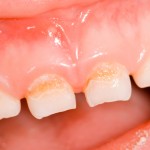
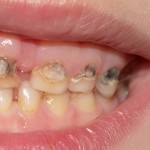
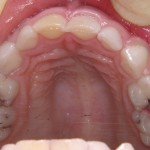
This review of the effectiveness of the mHealth-delivered oral health education to parents parents regarding the improvement of parents’ knowledge, behaviours and children’s oral health status included 12 studies. The studies findings were variable with some demonstrating benefit and some no benefit with all 8 of the included RCTs being at high risk of bias.
[read the full story...]