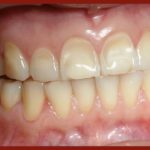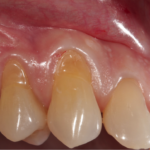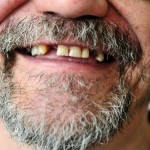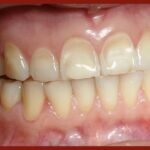
This review of the association between gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and dental erosion in children included 13 observational studies. The findings suggest positive association association between GERD and dental erosion in children however this should be interpreted cautiously because of the wide variety of diagnostic methods used in the included studies.
[read the full story...]