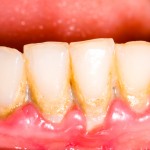
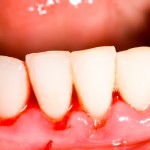
Twenty three systematic reviews were included in this overview of reviews reviews assessing the link between periodontal disease and adverse periodontal outcomes. While a majority of the available reviews suggest an association there are concerns regarding the quality of the primary studies.
[read the full story...]