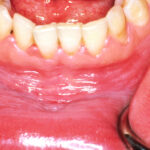
The prevalence of oral leukoplakia is estimated to be around 4% and is one of a number of oral potentially malignant disorders. Studies of malignant transformation in oral leukoplakia have shown highly variable rates ranging from 0.13% to 34.0%.
The aim of this review was to update an earlier systematic review (Dental Elf -24th Jul 2015) on the malignant transformation rate of oral leukoplakia.
Methods
Searches were conducted in the Cochrane Library, Embase, PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases. English language studies reporting on malignant transformation in patients with oral leukoplakia diagnosed by clinical and/or histopathological assessment were considered. Study screening and data extraction was carried out independently by two reviewers. Study quality was assessed using the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) tool and the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS). The primary outcome was the patients with oral leukoplakia who developed oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) Meta-analysis was conducted using a random-effects model.
Results
- 24 studies reporting a total of 16,604 patients were included.
- 14 studies were from Asia, 6 from Europe, 3 from America, 2 from Australia and one from Africa. One multicenter study included data from 3 countries.
- Malignant transformation (MT) in the individual studies ranged from 1.1% to 40.8%.
- Meta-analysis (26 studies) showed MT = 8% (95%CI; 7.9 to 11.7%).
- 10 studies analysed from first diagnosis of oral leukoplakia until the onset of the carcinoma with an estimated mean = 3.2 ± 0.9 years, with a range between 1.8 and 5.1 years.
- 6% of women and 37.4% of men developed OSCC (21 studies) with meta-analysis indicating an increased risk of MT = 1.65 (95%CI; 1.38 to 1.9).
- 16 studies considered presence of epithelial dysplasia in the initial diagnostic biopsy with meta-analysis indicating an increased risk = 23.8 (95%CI; 9.5 to 38.2).
- Tobacco and alcohol habits, betel quid, environmental nickel, location, and clinical type of oral leukoplakia were discussed.
Conclusions
The authors concluded: –
The pooled proportion of malignant transformation was 9.8% (95%CI; 7.9 to 11.7%). It is necessary to continue to conduct well-designed prospective clinicopathological studies on OL, using a uniform definition for OL to reduce the risk of bias for evaluating various factors associated with the MT.
Comments
The main aim of this review was to update an earlier review by Warnakulasuriya and Ariyawardana (Dental Elf -24th Jul 2015) and they found a pooled proportion of malignant transformation in oral leukoplakia of 9.8% (95%CI; 7.9 to 11.7%). This is almost the same rate reported in a 2020 review by Pinto et al (Dental Elf -6th Apr 2020) of 9.7% (7.8% to 11.7%). While the new review has only included English language paper they included 17 studies reported between 2015 and 2020 that were not included in the Pinto et al review. However, all the studies included in this new review are retrospective in nature as are the majority of studies included in the other reviews. There are also challenges in relation to the definitions and diagnostic criteria for oral leukoplakia. International agreement and implementation and reporting of consistent definitions would assist reviewers in future. In addition, well designed and reported prospective studies of appropriate size would provide better evidence relating to risk and predictive factors of malignant transformation in oral leukoplakia.
Links
Primary Paper
Aguirre-Urizar JM, Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza I, Warnakulasuriya S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the last 5 years. Oral Dis. 2021 Feb 19. doi: 10.1111/odi.13810. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33606345.
Other references
Dental Elf – 8th Aug 2018
Dental Elf -24th Jul 2015
Oral leukoplakia: malignant transformation rate highly variable
Dental Elf -6th Apr 2020
Photo credits
By Unknown photographer – This image was released by the National Cancer Institute, an agency part of the National Institutes of Health, with the ID 2583. Public Domain
