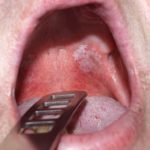
Oral leukoplakia is the commonest of a group of oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMDs) with a prevalence of about 4.5%. Studies report malignant transformation rates ranging between 0-20%.
The aim of this review was to determine the rate of malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia and assess the influence of demographic factors (age, gender, and geographic region) on the overall transformation rate.
Methods
Searches were conducted in the Cochrane Library, Embase, LILACS and PubMed databases. Observational studies assessing malignant transformation in oral leukoplakia were considered. Two reviewers independently screened and selected studies. Data extraction and assessment of study quality using the checklist for prevalence studies from the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) was also conducted independently by two reviewers. Findings were expressed as proportions or odds ratios (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) and meta-analyses conducted. Meta-regression was undertaken to identify possible sources of heterogenicity.
Results
- 34 studies (26 retrospective, 8 prospective) involving a total of 26,209 patients were included.
- Data was included from Australia, China, Croatia, Denmark, Hungary, India, Iran, Ireland, Italy, Japan, The Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Taiwan, the United Kingdom, the United States and Wales.
- 32 studies (23,489 cases, 1762 undergoing malignant transformation). contributed to the quantitative analysis.
| No of studies | Malignant Transformation Rate (95%CI) | |
| Overall mean rate | 32 | 9.7% (7.8% to 11.7%) |
| Male rate | 17 | 7.2% (5.0% to 9.5%) |
| Female rate | 17 | 12.6% (7.5% to 17.8%) |
- The odds of malignant transformation were lower for males than females OR = 0.62 (95%CI: 0.47 to 0.83)
- The average time to malignant transformation (17 studies) ranged from 11 to 132 months.
Conclusions
The authors concluded: –
The findings suggest the existence of a higher malignant transformation rate (MTR) than those reported by previous studies and that this rate is dependent on geographic region, gender (females with higher odds of oral leukoplakia (OL) undergoing malignant transformation), and follow-up period (longer follow-ups are associated with higher MTRs). Taking into account the outcomes and the limitations of this study, future research in the field of malignant transformation of OL should include the development of guidelines for conducting long-term follow-up studies to provide a more reliable methodology, thus reducing heterogeneity.
Comments
As good range of databases were searched for this review with the reviewers identifying 34 studies meeting the inclusion criteria. This represents 10 more studies with more than double the number of patients included than in an earlier review of this topic by Warnakulasuriya and Ariyawardana (Dental Elf – 24th July 2015). As with the earlier review the bulk of the included studies are retrospective (76%) which are at greater risk of bias. As the authors noted there is also heterogeneity in the definitions of and diagnostic criteria for oral leukoplakia across the studies. There was also heterogeneity in the reporting of potential risk factors (e.g., morphologic characteristics, tobacco consumption, and grades of dysplasia) across the included studies. This new review estimated a mean rate of malignant transformation on 9.7% which is lower than the 14.9% form the earlier review. In light of the quality of the available studies these estimates should be viewed cautiously.
In order to gain a better understanding of malignant transformation in oral leukoplakia well conducted and reported prospective studies or appropriate duration are needed. Developing a common reporting framework with standardised assessment of participants’ demographic characteristics, risk factors, and diagnostic (clinical and histologic) criteria as suggested by the authors would be helpful.
Links
Primary Paper
Pinto AC, Caramels Francisco H, Chen, A, Azul AM, Marques D. Malignant transformation rate of oral leukoplakia— systematic review Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2020 ( Article in Press) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2020.02.017
Review protocol on PROSPERO database
Other references
Dental Elf – 24th July 2015
Oral leukoplakia: malignant transformation rate highly variable
Dental Elf – 8th Aug 2018
Picture Credits
By Klaus D. Peter, Gummersbach, Germany – Own work, CC BY 3.0 de,
