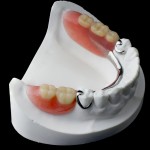
The shortened dental arch with ten pairs of occluding anterior and premolar teeth is considered sufficient to provide good oral function and is consistent with the WHO concept of a functional dentition without resort to a prosthesis.
The aim of this trial was to compare oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) in patients with either molar replacement by partial removable dental prostheses (PRDP) or with restored shortened dental arches (SDA) over 10 years.
Methods
This multi-centre randomised trial recruited patients from 14 dental schools in Germany. Patients age 35 and above in good general health requesting prosthodontic treatment with all molars missing in one jaw (study jaw), with at least both canines and one premolar present on each side of the jaw. Patients were block randomised to either the shortened dental arch (SDA) group or partial removable dental prosthesis (PRDP) group. Sample size calculation was based on tooth loss the primary outcomes of the trial (Walter et al 2018).
If the SDA was complete to second premolar to treatment was performed, in those with missing 2nd premolars teeth were replaced with conventional cantilever metal-ceramic fixed dental prostheses (FDP). In the PRDP group molar teeth were replaced using precision attachments connected to either splinted metal-ceramic crowns or conventional FDP abutments on the posterior-most teeth on both sides. Any missing tooth up to the first premolar was replaced by conventional metal-ceramic tooth-supported FDP in both groups. All other necessary care was provided with procedures being standardised across the centres. OHRQoL was assessed using the German translation of the 49-item Oral Health Impact Profile administered at baseline, 4–8 weeks, 6 months, 12 months, 24 months, 36 months, 48 months, 60 months, 96 months, and 120 months.
Results
- Of the 215 randomised 152 received interventions 81 in PRDP group and 71 in SDA group.
- OHRQoL substantially improved from baseline to first follow-up in both groups indicated by a mean decrease in OHIP scores of 20.0 points (95%-CI: 12.5-27.5).
- Compared to the SDA group, OHRQoL in the PRDP group was not significantly different (-0.6 OHIP points; 95%-CI: -7.1 to 5.9) during the study period when assuming a constant time effect.
- OHRQoL remained stable over the 10 years with a statistically insignificant time effect (p = 0.848).
Conclusions
The authors concluded: –
both SDA and PRDP are treatment options with long- lasting and clinically relevant effects on OHRQoL for a period of 10 years with no option being superior in terms of OHRQoL improvement in patients requesting prosthodontic treatment for their lost molars.
Comments
This study reports on the 10-year OHRQoL outcomes in a trail comparing SDA and PRDP treatment options. The main outcomes of the trial, tooth loss over 10 years, being reported in another paper (Walter MH et al 2018). The trial findings suggested little difference in the outcomes between the two different approaches after 10 years.
Links
Primary Paper
Reissmann DR, Wolfart S, John MT, Marré B, Walter M, Kern M, Kohal R, Nothdurft F, Stark H, Schierz O, Wöstmann B, Hannak W, Mundt T, Pospiech P, Boldt J, Edelhoff D, Busche E, Jahn F, Luthardt RG, Hartmann S, Heydecke G. Impact of shortened dental arch on oral health-related quality of life over a period of 10 years – A randomized controlled trial. J Dent. 2019 Jan;80:55-62. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 21. PubMed PMID: 30355509.
Other references
Walter MH, Dreyhaupt J, Hannak W, Wolfart S, Luthardt RG, Stark H, Pospiech P, Mundt T, Kern M, Böning KW, Wöstmann B, Scheller H, Jahn F, Reinhardt W, Strub J, Marré B, Heydecke G. The Randomized Shortened Dental Arch Study: Tooth Loss Over 10 Years. Int J Prosthodont. 2018 Jan/Feb;31(1):77-84. doi: 10.11607/ijp.5368. PubMed PMID: 29316570.
Dental Elf Blogs – Shortened dental Arch
