Katrina Witt summarises a recent nationwide cohort study, which suggests that infection, particularly with hepatitis, HIV or AIDS, is a significant risk factor for suicide.
[read the full story...]
Katrina Witt summarises a recent nationwide cohort study, which suggests that infection, particularly with hepatitis, HIV or AIDS, is a significant risk factor for suicide.
[read the full story...]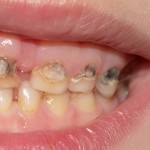
This review included 5 case-controlled studies only 2 of which were at low risk of bias and suggested that HIV-infected children have a higher risk of cavitated caries in their primary teeth, OR = 2.98, 95% CI; 1.59-5.59.
[read the full story...]
Oral Ulcers occur more frequently, last longer and produce more painful symptoms in HIV-infected adults. Aphthous ulcers are generally classified as major, minor or herpetiform. Major ulcers can exceed 3cm in diameter and can develop into large necrotic lesions. Major ulcers are seen more commonly in HIV-infected than non-infected adults. The aim of this Cochrane [read the full story…]

HIV/AIDS is currently the leading cause of death in adults in Africa and the sixth leading cause of death worldwide. In HIV infected adults, oral ulcers occur more frequently, last longer, and produce more painful symptoms than in immunocompetent people. The aim of this review was to evaluate the efficacy and side effects of topical [read the full story…]